SceneHub overview¶
The SceneHub is the name for a set of components allowing to create, process and render a scene. The SceneHub includes the following components:
- The SceneGraph is a generic KL-based scene graph which allows to define a hierarchy of objects and properties. The SceneGraph implements the Scene Assembly interfaces, allowing it to be queried and processed by a generic procedural graph. The SceneGraph can be populated by generators such as Alembic readers (AlembicToSceneGraph Extension).
- The Scene Assembly defines a set of interfaces to abstract a scene and allow generic processing of its elements.
It defines, too, a set of scene element queries and filter nodes which can define a scene processing procedural graph. The components that define or work with these abstracted scene interfaces are labeled with
SW, which stands for “Scene Wrapper”. - The RealTime Renderer defines a realtime renderer framework which is fast and flexible. It includes, too, components allowing to render scenes that are defining the Scene Assembly interfaces. The SceneGraphToRTR Extension defines specialized adaptors for mapping higher-level scene graph types (wrappers) to RealTime Renderer objects.
All these define KL runtime components of the SceneHub, but don’t include specific UI or tools. The sceneHub application provides a
simple base application for exploring SceneHub, and provides a basic implementation of tools such as selection and transform.
Additionally, it can be used to launch samples, for example sceneHub /Samples/RTR2/GeneratedInstances.kl.
警告
The SceneHub and its components is a work in progress, and is still missing various functionality, examples, documentation. Although its general design should not change, it will continue to evolve.
From SceneGraph to RTR¶
The following image illustrates an overview of the data flow from the scenegraph to the RealTime Renderer. The SceneGraph data is being filtered and processed by Scene Assembly components:
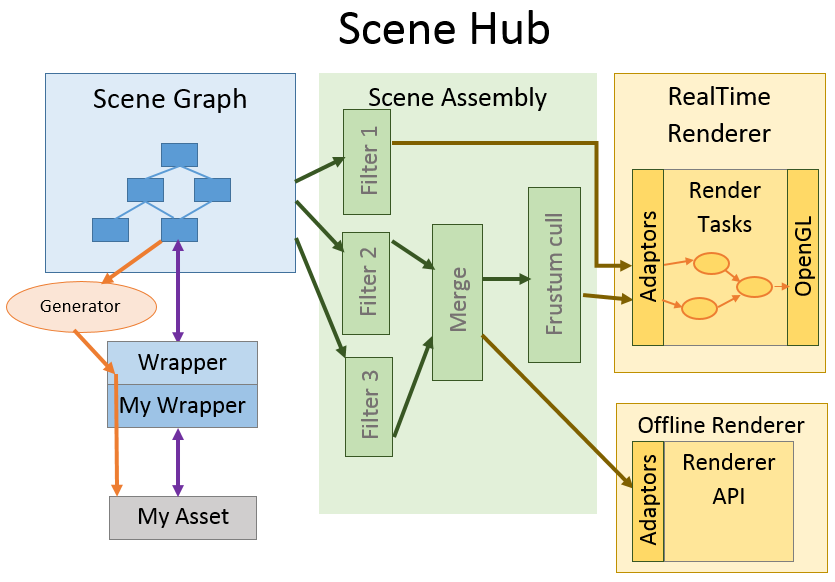
The following steps are illustrated:
A
SceneGraphstructure is defined, which includes multiple scene graph objects (SGObject) and their relationships. The scene graph objects are associated with higher-level wrappers which define concrete behavior and features for the scene graph object. In this example, “My Wrapper” defines an intermediate between a the “My Asset” custom asset object and the scene graph. A generator is associated with the scene graph object so that the data can be fetched only when requested by the Scene Assembly or RealTime Renderer.SceneGraph objects are extracted by a Scene Assembly query. The resulting elements are returned as an array of scene element references (
SWElementReference). These scene element references are lightweight and link directly to the related SceneGraph object or property. They provide a generic functionality such as getting a sub-property or getting the underlying value or interface.Various filters and processing Scene Assembly nodes will further refine the selected data. These processing nodes support incremental and asynchronous changes, which is a functionaity provided by their base class (
BaseDynamicGroup). The provided generic nodes are using the abstractedSceneWrapperinterfaces, however they can be specialized to provide a specific behavior (eg: RTR2 definesRTRCullFromCameraTaskwhich culls based on the volume of anRTRCamera).警告
The set of provided processing or filtering nodes at this point is pretty limited, for example these don’t include nodes to “merge” multiple scenes together. Additionally, DFG support for the assembly graph is planned but hasn’t been realized at this point.
Finally, the RealTime Renderer will create rendering objects (such as instances or lights) corresponding to the provided set of scene element references. Specific render object adaptors will be created depending on the type of the referenced scene elements, using an adaptor registry mechanism (see Scene element adaptors). The RealTime Renderer will further process the scene elements with its own task graph (
RTRTask) in order to generate the required drawing data and effects.
See Scene Assembly for more details about procedural scene processing.
Scene element adaptors¶
A fundamental concept of the SceneHub is the usage of adaptors. An adaptor is a KL Object
(usually an ObjectAdaptor) which provides a data cache and functionality bridge
between a specific source scene element type and a specific target (eg: OpenGL RealTime Renderer
or a specific offline renderer).
The goal of adaptors is to provide specialized functionality and data cache
for mapping a source specialized type to a required target, which allows to have
custom objects properly translated by generic processing tasks. For example,
a source Vec3AttributeToRTR adaptor will associate a Vec3Attribute
with an OGLBuffer_ shared cache. Similarly, the SGDirectionalLightToRTR
adapts a SceneGraph-specific SGDirectionalLight to a RTR-specific
RTRDirectionalLight.
Adaptors are registered with the RegisterAdaptor global function, and
can be created by the CreateAdaptor global function (these internally use a global
factory object: AdaptorRegistry). Adaptors must be registered
before they can be created.
The SWElementReference allows to create and attach adaptors to source scene items
(SWElementReference.getAdaptor) and updates them. The adaptors remain attached
to the scene element itself, so different SWElementReference referring the same
scene element will share a same adaptor. It is possible, however, that a different adaptor
is returned for different evaluation contexts (animated value).
SceneGraph to RTR adaptors example¶
The example below illustrates the components involved in creating adaptors from the SceneGraph to the RTR:
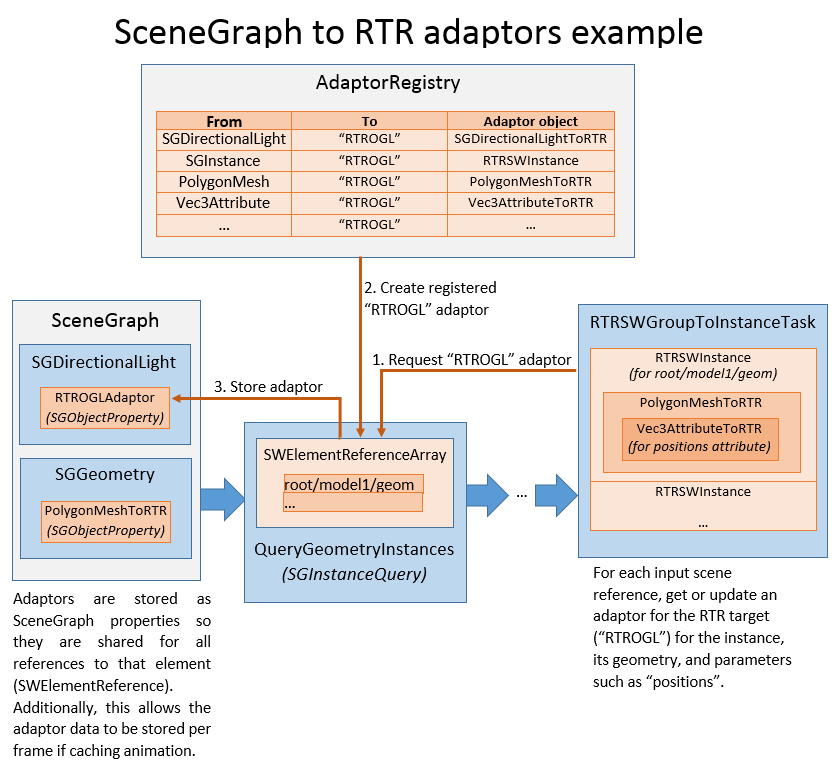
In the diagram above, the following steps are shown:
- The
RTRSWGroupToInstanceTaskrequests adaptors for mapping SceneGaph objects to RTR objects. More precisely, it needs to creates a RTRInstance for each inputSWElementReference(stored in aSWElementReferenceArray), and gets an adaptor for the “RTROGL” target. - The
SWElementReferenceArrayasks theAdaptorRegistryfor an adaptor from aSGGeometryto an “RTROGL” target, and gets aRTRSWInstance. It stores a reference of this adaptor in the SceneGraph, associated with the sourceSGGeometryobject so it is shared for all references. - The
RTRSWGroupToInstanceTaskupdates theRTRSWInstance, which recursively creates an adaptor for the underlying geometry (PolygonMeshToRTR) and for the postions attribute (Vec3AttributeToRTR).
